In dental discussions about upcoming procedures, dentists often mention platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. This innovative therapy accelerates the healing of both hard and soft tissues in the oral cavity.
Its proven efficacy has established it as a standard of care for tooth extractions, implants, and various dental procedures.
Plasmolifting World has developed applicable therapeutic protocols used in the following areas of treatment:
- Aesthetic medicine
- Dentistry
- Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Trichology
Within dentistry, both PRP and PRF therapies play pivotal roles in expediting recovery post-specific dental procedures. Let us delve deeper into these two processes to better understand their applications.
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) revolutionizes tissue regeneration and wound healing in dental and oral surgery, including procedures like tooth removal and dental implants. Widely adopted in dentistry, PRP significantly aids post-oral surgery recovery.
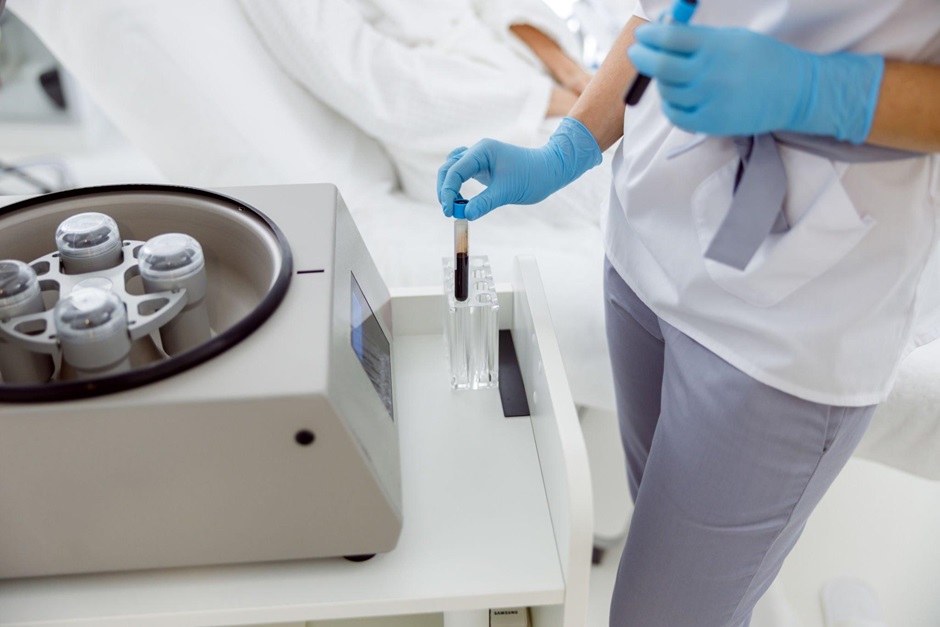
Derived from the patient’s blood, PRP is plasma enriched with platelets, strategically applied to bone defects.
The PRP gel, created by combining plasma with thrombin and calcium chloride, accelerates healing by injecting concentrated platelets into damaged areas, promoting tissue repair.
Benefits:
- Safe, with no documented cases of infection risk, illness transmission (including HIV and hepatitis), adverse responses, or adverse effects.
- PRP’s growth factors aid in boosting tissue synthesis, which speeds up tissue regeneration.
- A dental practitioner with training can prepare PRP simultaneously with the procedure. Therefore, it does not take long.
- It is easily obtainable.
- Because PRP makes bone grafting goods and substitution materials more gel-like, it makes them easier to apply and handle.
- PRP enhances bone grafting for dental implants and proves beneficial in diverse restorative dentistry procedures, including closing cleft lips and addressing defects from tooth removal or cyst/fistula removal.
Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF)
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) is a groundbreaking contributor to tissue regeneration and wound healing in dental and oral surgery, spanning procedures such as tooth removal and dental implants.
PRP significantly enhances post-oral surgery recovery, highly valued in dentistry, comprising plasma enriched with platelets derived from the patient’s blood.
Applied strategically to bone defects, the PRP gel, formed with thrombin and calcium chloride, accelerates natural healing processes, injecting concentrated platelets into damaged areas for effective tissue repair.
Benefits:
- Through the recruitment of osteoblasts, or bone-forming cells, to the affected area, PRF aids in the restoration of peri-implant bone.
- It aids in maintaining the alveolar ridge.
- PRF helps to mend periodontal abnormalities and produces new bone, enhancing your teeth’ condition.
- Because PRF can rebuild bone abnormalities following cancer surgery, it is helpful in the treatment of oral cancer.
- PRF increases gum volume, which aids in gum regeneration.
- Because PRF has antibacterial qualities, it aids in preventing and treating infection. It also repairs mucosal (soft tissue) edges by connecting them, a process that sutures cannot.
- PRF expedites the healing of wounds.
- According to some research, PRF is most likely the sole substance that can raise maxillary sinus floors.
- Osteitis, or inflammation of the bone, can be reduced by 90% with PRF.
Conclusion
In dental procedures, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) therapies are integral for accelerated recovery.
PRP aids in tissue regeneration, while PRF contributes to bone restoration, alveolar ridge maintenance, and gum regeneration.
These safe and efficient therapies are paramount in various dental applications, ensuring enhanced healing and improved outcomes.





Comments